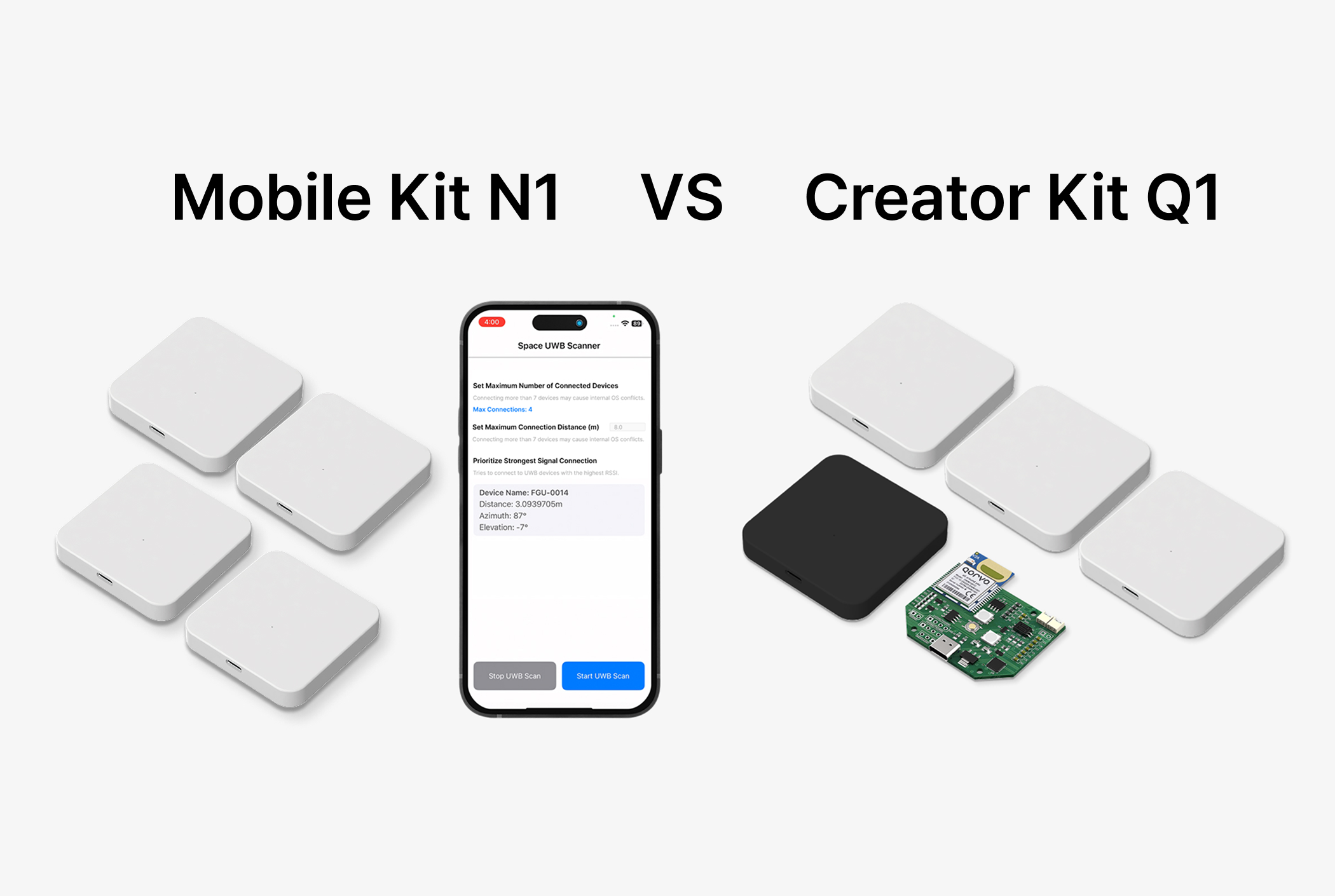
Recently, the need for precise indoor positioning technology has been increasing across various industries such as smart factories, logistics, healthcare, and autonomous robots.
Traditional wireless communication technologies such as GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth have limitations in indoor environments, making stable and accurate positioning difficult. As a solution, Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology is gaining attention.
This document provides an in-depth exploration of UWB technology, its differences from existing technologies, and its applications across industries.
What is UWB?
UWB (Ultra-Wideband) is an advanced high-precision indoor positioning technology that offers greater accuracy and stability compared to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
- Provides positioning accuracy within a 10–30 cm margin of error
- Operates with low power consumption for efficient wireless communication
- Offers stronger signal transmission and security than Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Traditional GPS works well outdoors but suffers from weakened signals and reduced accuracy indoors.
In contrast, UWB provides high-precision positioning even in indoor environments, making it an essential technology for smart space development.
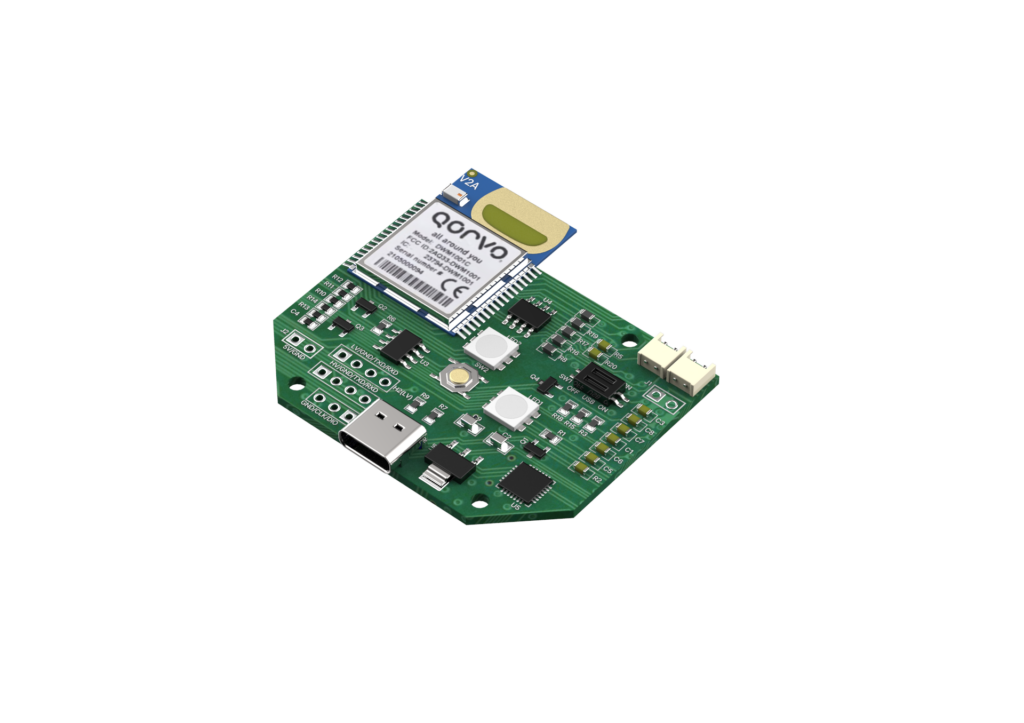

How UWB Works
UWB is a wireless communication technology that transmits data at low power using an ultra-wide frequency band (500 MHz or more).
Unlike Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, which transmit continuous signals, UWB sends short pulses for signal transmission.
This results in:
- Faster data transmission
- Minimal signal interference
- Extremely precise distance and location measurements
In summary, UWB is not just a wireless communication technology—it is a next-generation solution for accurate positioning and indoor networking.
How UWB Measures Distance
UWB determines distance using the Time of Flight (ToF) measurement method, which calculates the time it takes for a signal to travel between two points.
ToF (Time of Flight) Measurement Process
- The UWB tag transmits a signal
- The anchor receives the signal
- The time taken for the signal to travel is measured
- The distance is calculated using the speed of light (accuracy within 10–30 cm)
This principle is similar to how an echo travels back when shouting in the mountains.
By precisely measuring the time it takes for the signal to travel, UWB can achieve highly accurate indoor positioning.
UWB vs. Traditional Wireless Technologies
| Technology | Positioning Accuracy | Transmission Speed | Power Consumption | Security | Indoor Usability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth (BLE) | 1–5m | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Wi-Fi | 5–10m | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate |
| RFID | 50cm–several meters | Slow | Low | Moderate | Low |
| GPS | 3–10m (Not for indoor use) | Fast | High | Moderate | Not usable |
| UWB | 10–30cm | Very fast | Low | Very high | Very high |
UWB has lower power consumption than Wi-Fi, higher security than Bluetooth, and offers highly accurate positioning even in indoor environments where GPS fails.