Hello, this is Freegrow.
Today, we’re going to take a closer look at one of the questions many people ask: what’s the difference between GPS and RTK GPS? We’ll break it down in a simple way and also share the latest use cases as of 2025.
Among all the positioning technologies we use every day, GPS is by far the most familiar. When you turn on navigation in your car or check a delivery rider’s location on an app, that little blue dot moving in real time feels incredibly convenient.
But you’ve probably experienced this before: your navigation says you’re on this road, but in reality you’re actually on the next street over. Or the location marker jumps around when you’re near tall buildings. This is the limitation of standard GPS.
Standard GPS: Technology that Shows “Around Here”
GPS (Global Positioning System) works by satellites sending signals down to Earth. Your smartphone or device receives these signals and calculates its position through trilateration.
The problem is, satellite signals aren’t perfect. As they pass through the atmosphere, delays occur, and in cities signals bounce off tall buildings or mountains, causing distortion. This is why your location can be off by several meters.

In short, regular GPS doesn’t say “exactly here” but more like “somewhere around here.” The usual error margin is between 3–10 meters. For everyday navigation, this is fine. But in cases like autonomous driving, where lane-level accuracy is needed, or drone surveying, which requires centimeter-level precision, such errors are unacceptable.
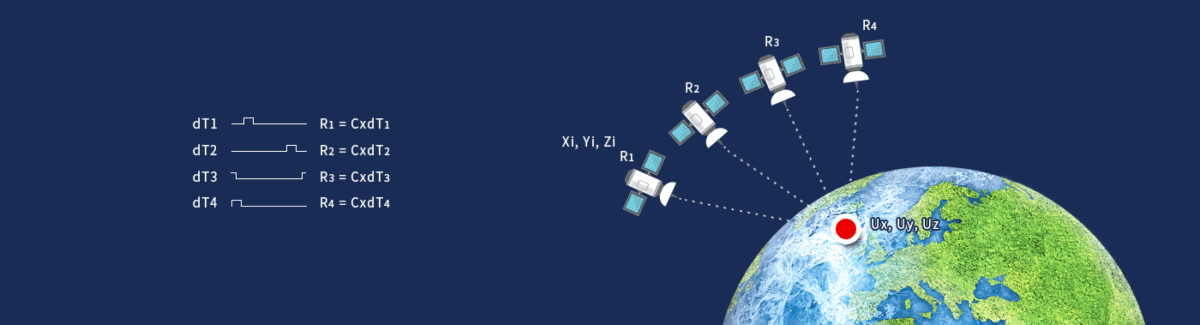
RTK GPS: Real-Time Precision Down to Centimeters
This is where RTK GPS (Real-Time Kinematic GPS) comes in.
Here’s how it works:
- A base station receives satellite signals and compares them with its known position.
- It calculates the errors in real time.
- Correction data is then transmitted to the rover (the device you’re using).
Think of it this way: the base station says, “the signal is off by this much,” and your device adjusts accordingly.
Thanks to this correction, RTK GPS reduces error to just a few centimeters—often as little as 1–2 cm. If GPS tells you “around there,” RTK GPS pinpoints “right here.”
GPS Satellites in 2025
Globally, GPS is well-established. As of June 2025, a total of 32 GPS satellites are in orbit, with 31 active. This ensures that users almost anywhere on Earth can access 5–8 satellite signals at the same time.
So the satellites themselves are not the issue—the difference in accuracy comes from whether or not RTK correction is used.
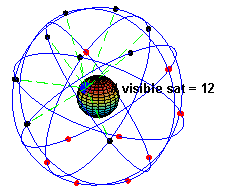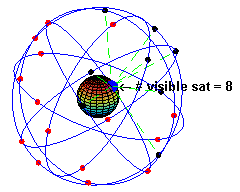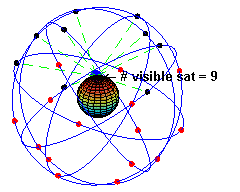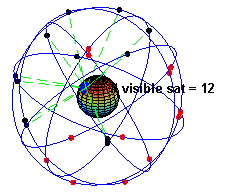
GPS vs RTK GPS: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Category | Standard GPS | RTK GPS |
|---|---|---|
| Position Accuracy | 3–10 m error | 1–2 cm precision |
| Calculation | Device only | Base station correction |
| Required Satellites | Minimum 3–4 | Same (but corrected) |
| Use Cases | Navigation, delivery tracking | Autonomous driving, drone surveying, smart farming, construction |
Why RTK GPS Matters – The Power of Precision
For everyday use like finding your way, GPS is good enough. But in industrial and safety-critical environments, the difference is huge:
- Autonomous Vehicles → Lane-level recognition, stopping at the exact line.
- Drone Surveying → High-precision 3D scans of construction sites.
- Smart Farming → Tractors automatically plowing straight lines and planting at perfect intervals.
- Precision Construction → Roads, railways, and bridges where even centimeters matter.
In short, RTK GPS isn’t just a convenience—it’s essential infrastructure for safety and efficiency.
Real-World Examples of RTK GPS
On a construction site I visited, survey teams once had to spend an entire day manually collecting coordinate points. With an RTK GPS-enabled drone, they captured hundreds of thousands of points in just a few hours, creating a 3D model with ±2 cm accuracy.
In smart farming, RTK GPS-powered tractors followed precise straight paths and maintained consistent spacing during planting, significantly improving productivity.


Can Everyday Users Access RTK GPS?
In the past, RTK GPS was only available in expensive professional equipment. Today, it’s becoming more accessible:
- Smartphones → Some recent models can directly receive RTK correction signals.
- Drones → DJI and other commercial drones offer RTK modules for mapping and 3D modeling.
- Smart Farming → Most autonomous tractors now come with RTK GPS as standard.
And with Freegrow’s RTK Modem, even general users can set up and test RTK GPS environments easily. Just connect the modem to a base station, and you can experience hybrid indoor/outdoor high-precision positioning right away.
Conclusion – The Era of Precision Location, Led by RTK GPS
Standard GPS is convenient for daily life, but for industries and next-generation services, centimeter-level accuracy is non-negotiable.
RTK GPS is already proving its value in autonomous driving, drone surveying, smart farming, and precision construction. It’s becoming the foundation of future innovation.
At Freegrow, we provide solutions that integrate RTK GPS with UWB RTLS, enabling seamless precision positioning both indoors and outdoors. From smart factories to autonomous vehicle testing, we help industries unlock new possibilities in location accuracy.
The era of precision location is here, and RTK GPS is at the center of it.